Using Stored Procedures in Coalesce
Overview
A Stored Procedure is a reusable block of SQL code that can be stored and executed. Stored procedures are used to perform specific tasks as part of a data pipeline, and they can be created, deployed, and called through a custom node type.
This guide details the steps to accomplish this in Coalesce, as well as provides the code for the custom Node Type used in this technique.
Creating a Stored Procedure
This custom Node Type takes a user-defined piece of SQL and executes it during Coalesce's Create and Deploy process. The SQL provided will be the create SQL for the Stored Procedure.
-
Create a custom Node Type by going to Build Settings > Node Types and clicking Create Node Type. Update the Node name to something that will help you remember the functionality.
-
Add in the code into the Node Definition and the Create Template. The Run Template is blank. Using the
deployStrategy: advancedwill give you a Current State and Desired State. You can ignore these.- Node Definition
- Create Template
capitalized: CREATE SQL
short: SQL
plural: SQLs
tagColor: '#2EB67D'
deployStrategy: advanced
config:
- groupName: 'Options'
items:
- type: textBox
displayName: SQL
attributeName: SQL1
syntax: sql
isRequired: true
systemColumns:
- displayName: SQL_SEQ
transform: ''
dataType: NUMBER IDENTITY
placement: beginning
attributeName: isSurrogateKey
- displayName: SYSTEM_START_DATE
transform: CAST(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP AS TIMESTAMP)
dataType: TIMESTAMP
placement: end
attributeName: isSystemStartDate{% if desiredState == currentState %} {{ stage('Nothing to do.') }} SELECT 1 = 0{% elif desiredState != undefined %} {{
stage('Create SQL1') }} {{ desiredState.config.SQL1 }} {% elif currentState != undefined and desiredState == undefined
%} {# Stored Procedure Name #} {% set targetObjectDatabase = ref_no_link(currentState.node.location.name,
currentState.node.name).split('.')[0] %} {% set targetObjectSchema = ref_no_link(currentState.node.location.name,
currentState.node.name).split('.')[1] %} {% set fullyQualifiedTargetObjectName =
ref_no_link(currentState.node.location.name, currentState.node.name) %} {{ stage('Drop SQL1') }} DROP PROCEDURE IF
EXISTS {{ fullyQualifiedTargetObjectName }} (VARCHAR){% else %} {{ stage('Unknown State') }} SELECT 1 = 1{% endif %}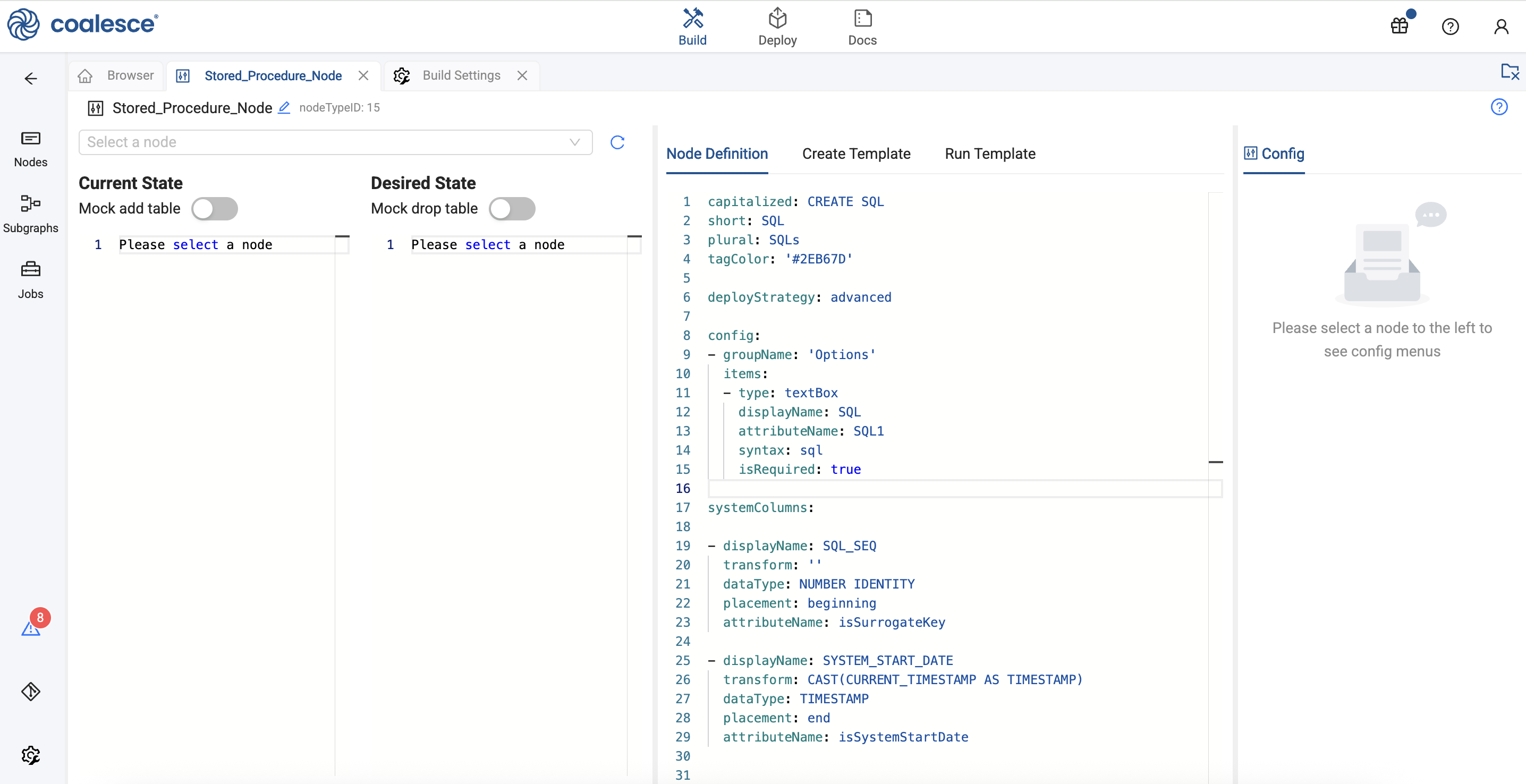
Add the code to the Node Definition and Create Template -
You need to update the Workspace macros. Go to Build Settings > Workspace Macros. Add the following code.
{#-- The below block of code initialises variables in case of node typess using advance deployment strategy #}
{% if desiredState %}
{% set columns = desiredState.columns %}
{% set storageLocations = desiredState.storageLocations %}
{% set config = desiredState.config %}
{% set sources = desiredState.sources %}
{% set node = desiredState.node %}
{% set parameters = desiredState.parameters %}
{% endif %}
{#-- The below block of code initialises variables in case of node typess using advance deployment strategy #}
{% if desiredState %}
{% set columns = desiredState.columns %}
{% set storageLocations = desiredState.storageLocations %}
{% set config = desiredState.config %}
{% set sources = desiredState.sources %}
{% set node = desiredState.node %}
{% set parameters = desiredState.parameters %}
{% set this = desiredState.this %}
{% endif %}
{#-- Macro to return node name #}
{#-- Input parameters - None #}
{#-- Return - Order by clause #}
{%- macro node_name() -%}
{{ ref_no_link(node.location.name, node.name) }}
{%- endmacro -%}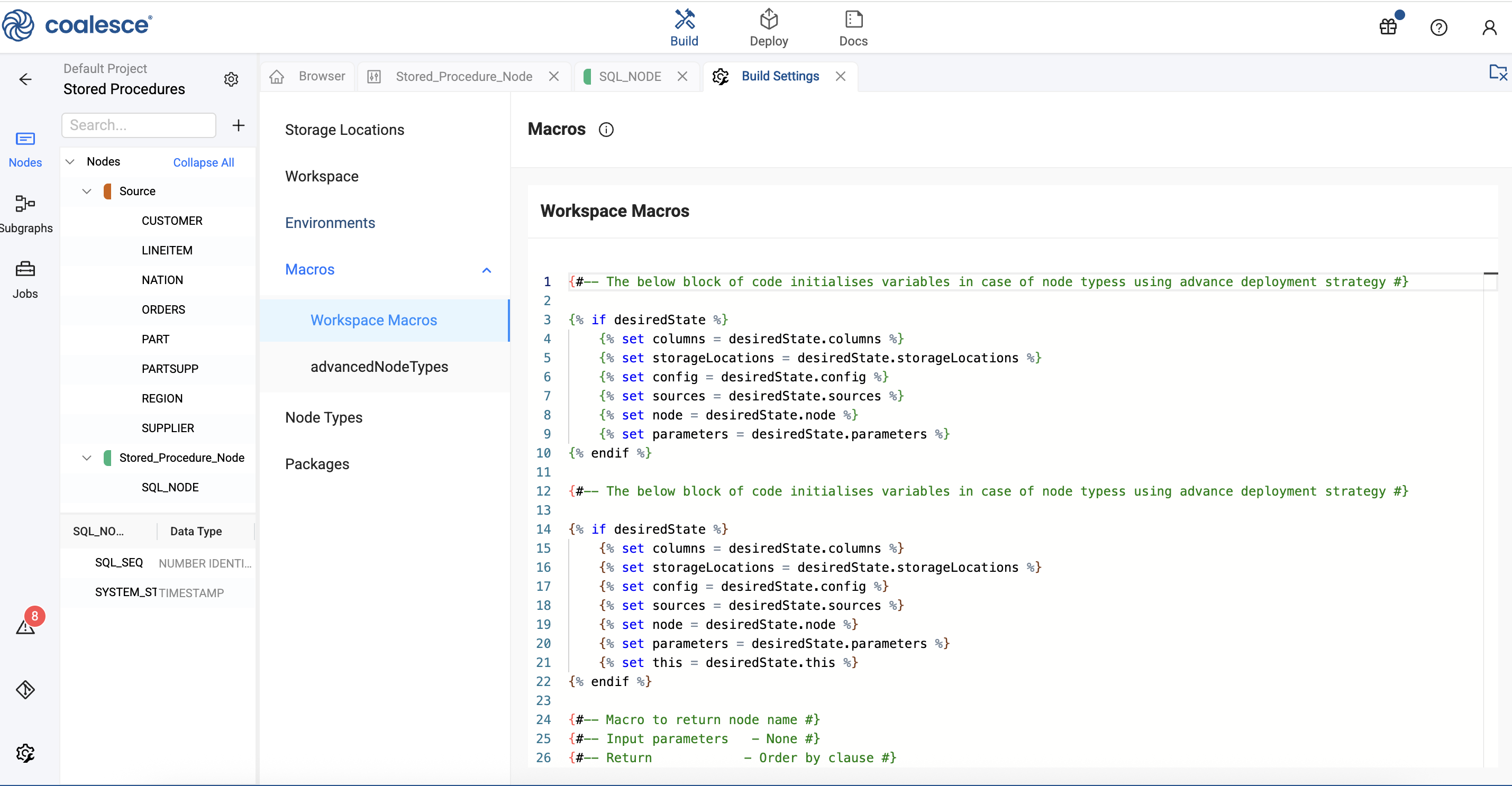
Add to Workspace Macros -
In the Mapping Grid, click the plus sign ‘+’ to Create New Node > Stored Procedure Node you created.
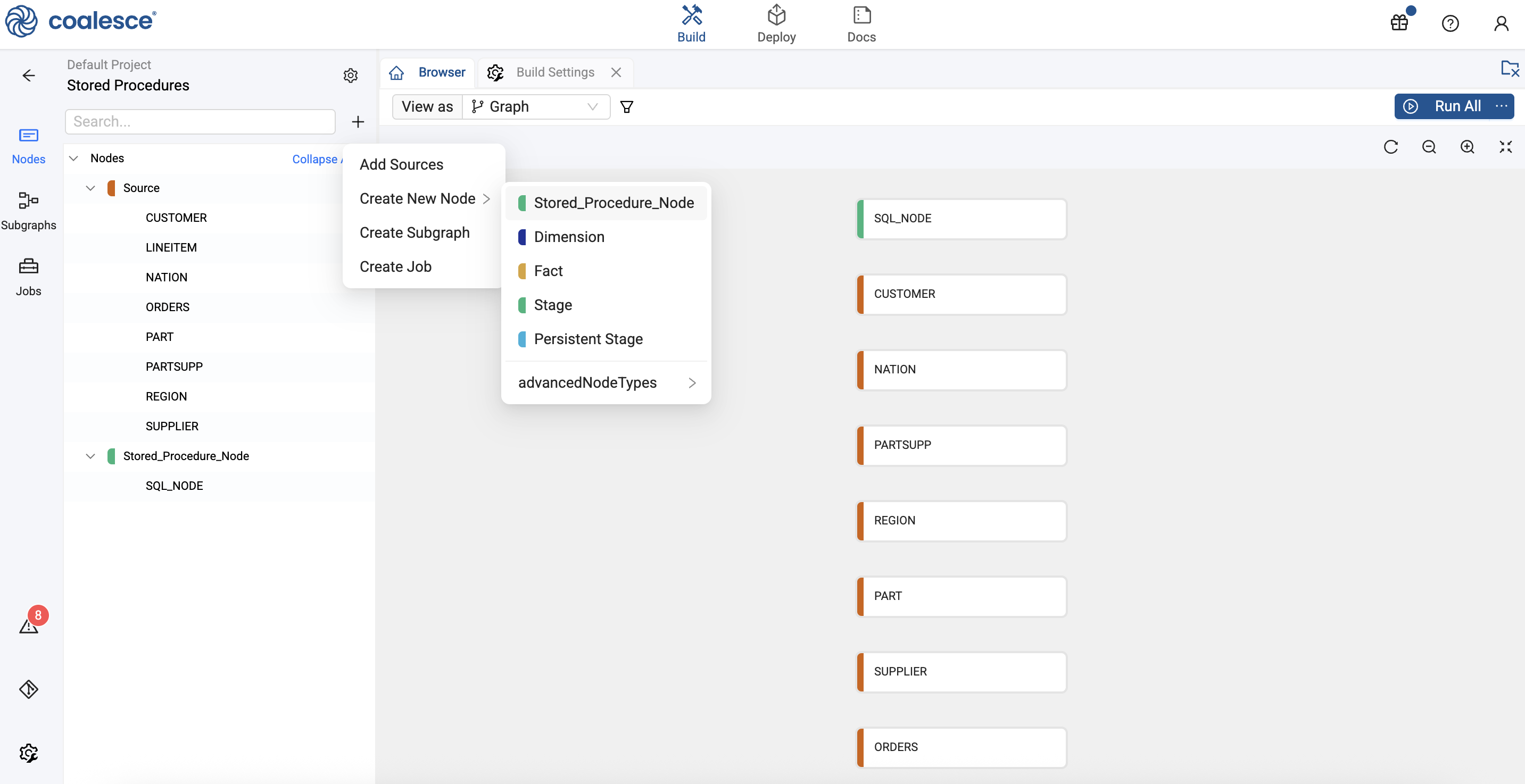
Add the Store Procedure Node. In this example it's SQL_NODE. -
In Node Properties, update the Storage Location. The Storage Location is where the Stored Procedure will be created in Snowflake.
-
In Options > SQL, you'll add the Data Definition Language (DDL) for the Stored Procedure. In this example, we are returning a message string.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE {{ node_name() }}("MESSAGE" STRING)
RETURNS STRING
LANGUAGE SQL
EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS '
begin
return message;
end;
';
-- Can also use {{this}}
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE {{this}} ("MESSAGE" STRING)
RETURNS STRING
LANGUAGE SQL
EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS '
begin
return message;
end;
'; -
Click Create, to create the Node, and check the results.
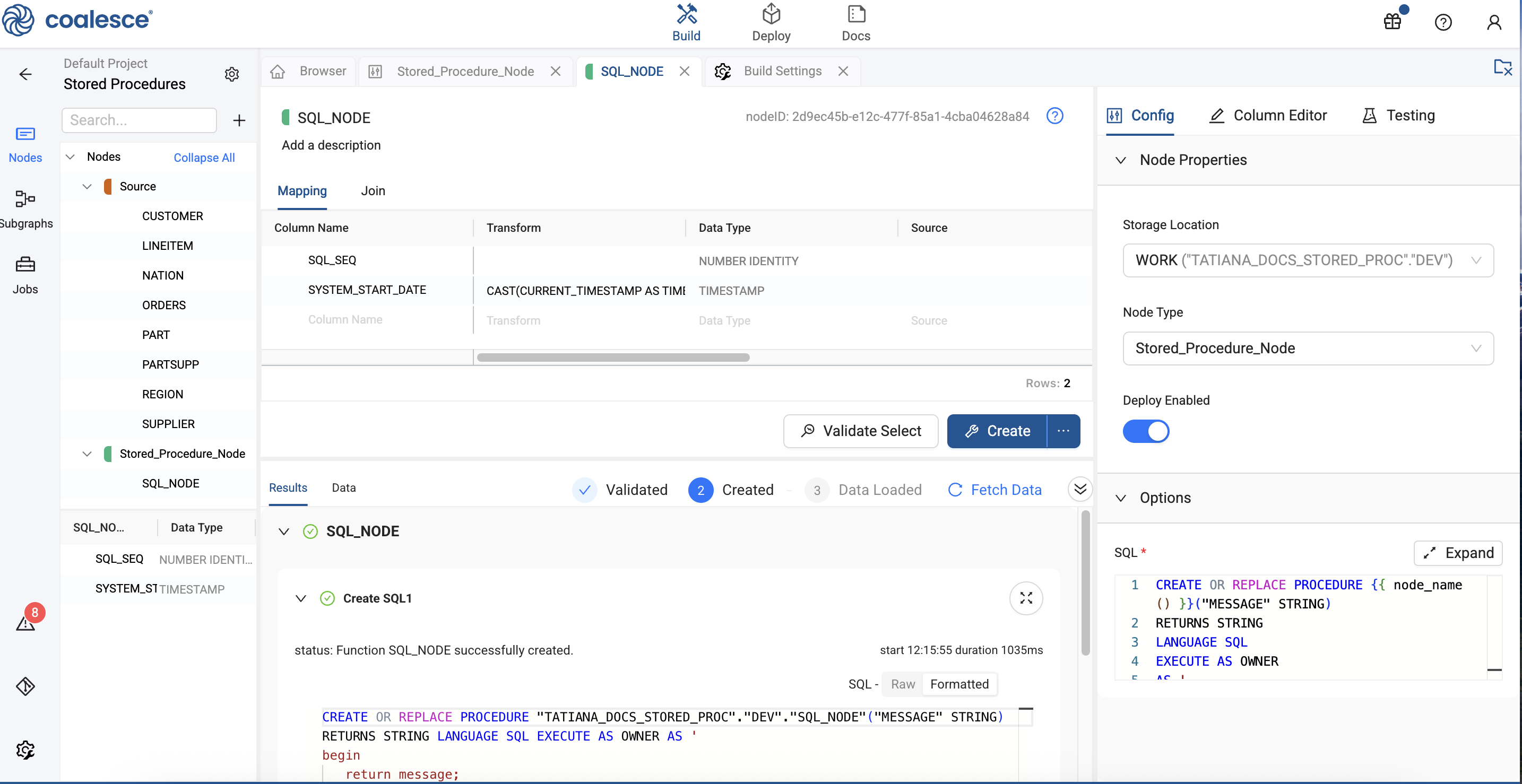
If you’re encountering errors when trying to create your Node, check the Storage Location for the stored procedure.
Calling the Stored Procedure
You can use a stored procedure in one of the following ways:
- As a piece of pre-SQL or post-SQL within a related Node.
call my_sp('param_one', 'param_two', 'param_three');
- As an independent Node. You would need to add a Run Template to the custom Node Type.
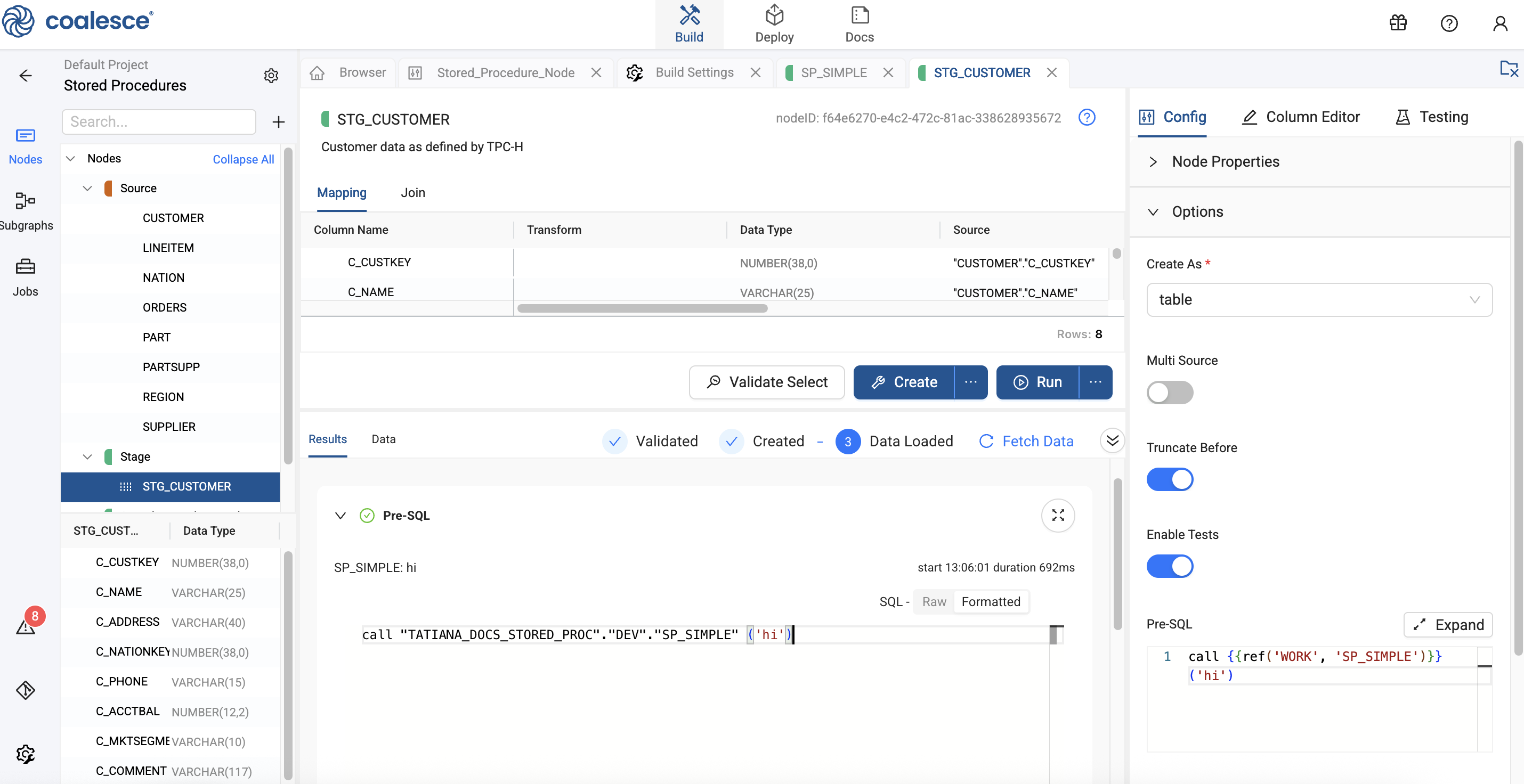
In this example, the Stored Procedure Node is called in the Pre-SQL.
call {{ref('WORK', 'SP_SIMPLE')}} ('hi')
Deploy the Stored Procedure
- Commit your Stored Procedure.
- Choose the Environment for deployment.
- Initiate the deployment from the chosen branch in Git.
- The deployment process will automatically create the Stored Procedure in the selected Environment.
Please be aware that the stored procedure will be included in every build, even when using advanced deployment options.