Storage Locations and Storage Mappings
Storage Locations and Storage Mappings are closely related but serve different purposes in managing and structuring data within Coalesce.
Storage Location and Mapping Best Practices
Storage Location
A Storage Location in Coalesce represents a logical destination for the database objects you use as sources and create within the platform. It acts as a container or grouping for these objects, such as views and tables, allowing you to organize and manage them effectively. Each Coalesce node, which represents a specific database object, is mapped to a single Storage Location. However, a single Storage Location can be mapped to multiple Nodes, providing flexibility in organizing your data.
Storage location mapping definitions are committed in Git for Environments, not for Workspaces.
Storage Mapping
Storage Mapping is a physical destination within your database that is defined for a Storage Location in a given Workspace or Environment. It represents the actual database and schema where the Storage Location resides. It allows you to define the exact location where your database objects will be stored within your Data Platform.
By using Storage Locations and Storage Mappings in Coalesce, you can achieve granular control over the organization and storage of your database objects. You can map different Storage Locations to different physical locations, enabling you to tailor the storage of your data based on specific requirements.
For example, in a development workspace, you can map each of your Storage Locations to the same physical location, effectively placing all database objects in a single schema used as a scratch working area.
Meanwhile in production, you can map each Storage Location to a different physical location for each storage location, allowing for the use of roles on specific schemas to control access to objects.
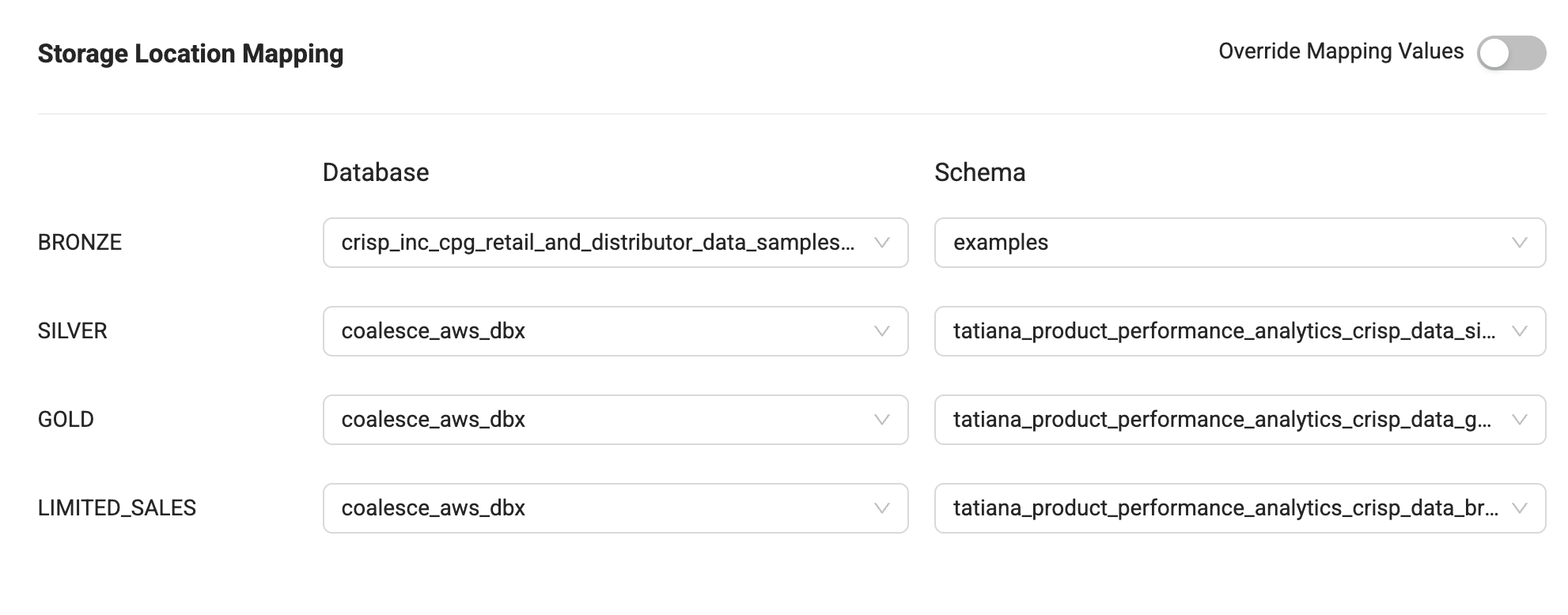
Example of Storage Location and Storage Mappings
In this example, one of the Storage Locations created is SILVER and it's mapped to the database and schema coalesce_aws_dbx.tatiana_product_performance_analytics.
Storage Location Versus Storage Mappings
| Storage Location | A logical destination for the objects you use as sources for and create within Coalesce. For example, views and tables in the form of Nodes. Each Coalesce Node is mapped to a single Storage Location, but a single Storage Location may be mapped to many Nodes. | Logical, and does not reconcile to a specific physical database or schema. Physical mappings are defined in Storage Mappings. Typically scoped or organized by a the database and schema structure in your account, but is environment independent. For example: SOURCE_SALESFORCE and DWH_SALES vs. UAT_SOURCE_SALESFORCE and UAT_DWH_SALES |
| Storage Mapping | A physical destination, database and schema that is defined for a Storage Location for a given Workspace or Environment. | Physical, environment specific mapping of a logical Storage Location at the database and schema level Reconciles to a specific physical database or schema. For example, the Storage Location SOURCE_SALESFORCE in your UAT Environment has a Storage Mapping of database UAT_SOURCE and schema SALESFORCE. |
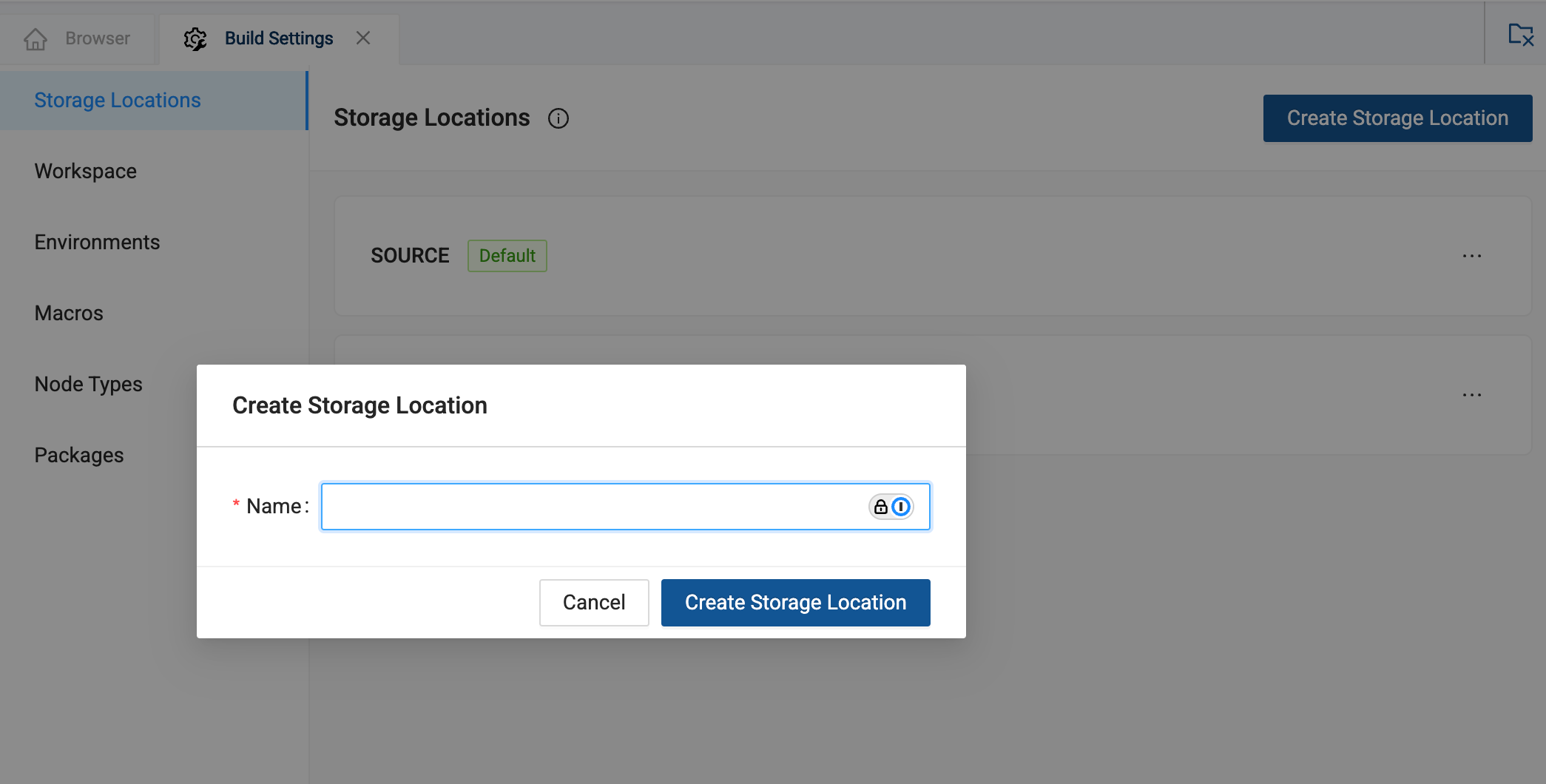
Add a Storage Location
- Launch your Workspace.
- Go to the Build Settings, .
- Click on Storage Locations.
- You can create as many Storage Locations as you need. It's a good idea to have a source data storage location and a transformation storage location. A best practice is to separate your Nodes into different storage locations that represent different groupings of datasets and to name them appropriately.
Create or Edit Storage Mappings
When adding sources in the build interface, only physical locations that are mapped to a Storage Location for that environment or workspace are available to be added. This means that you will need to define a Storage Location for source tables and map that to a physical location for that environment or workspace. Make sure you have configured your Storage Locations and connected to your data platform. Then you can map the physical locations in your Data Platform to the Storage Locations you created in Coalesce.
- Go to Build Settings, .
- Click Workspace Settings , and go to Storage Mappings.
- Any Storage Locations will be listed here. You can create as may mappings and locations as needed.
- Now you can map your database to the Storage Location. Choose the database location you want to map to your Storage Location.
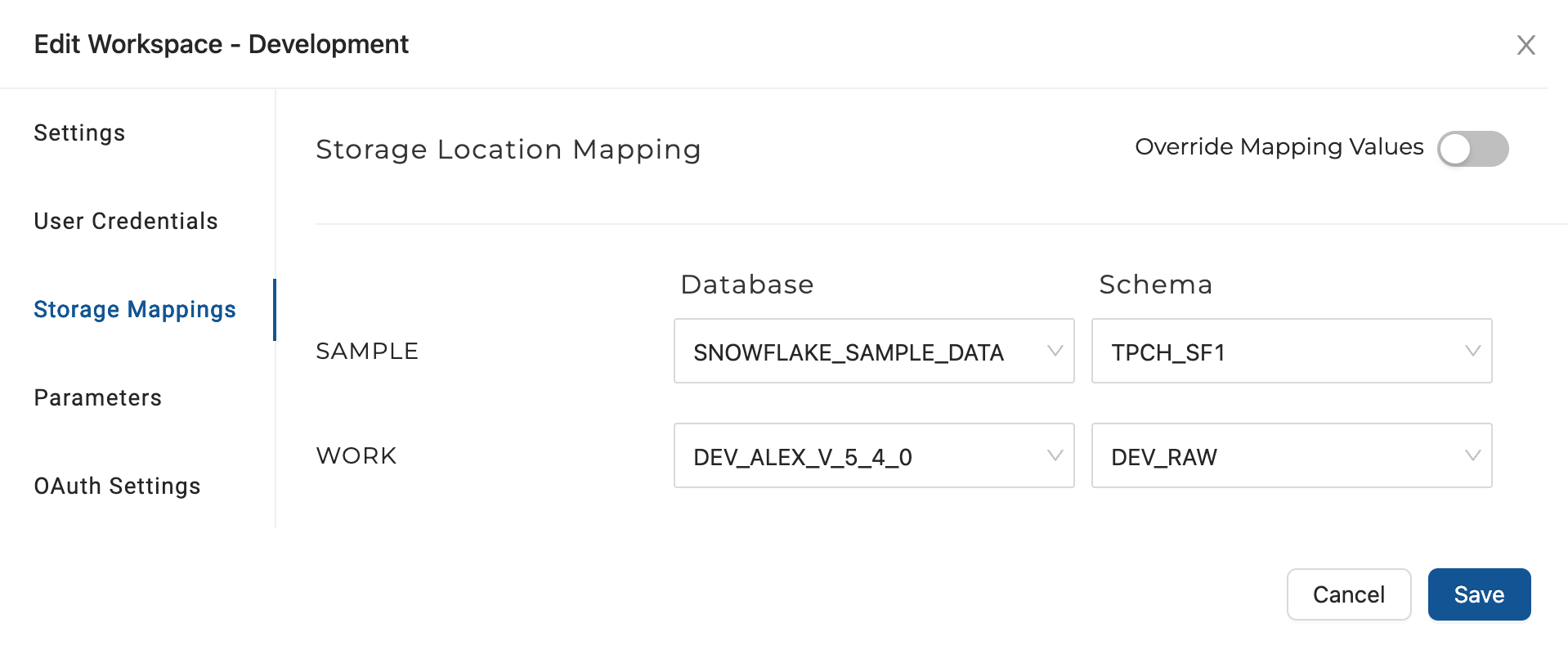
Override Mapping Values
To input database and schema objects manually, instead of choosing them from the dropdown menu, activate the Override Mapping Values option. This step may be necessary when mapping to a database or schema for which you lack access permissions.
Changing Your Database or Schema or Edit Storage Mappings
If you need to update the information from your data provider, here are a few tips.
- Always create a new database or schema.
- After creating the new schema, change the Storage Mappings to match the new schema and deploy the changes.
- The deploy process will recognize the Storage Mappings change and update the Nodes from the old schema to the new one.
Do not change existing deployed database or schema information. This will cause errors in Coalesce. Always create a new database and then update the Storage Mappings.