Column Transforms
Transforms are optional pieces of logic that can be applied to a column to either alter its data or generate new separate data.
Supported Transformations
Coalesce supports all transformation functions supported by your data platform. Transformation logic can be authored in several ways:
- Inline by double-clicking in the Transform field.
- Within the Column Editor.
- Using Macros to encapsulate logic and reduce code duplication for frequently used transformations.
By default, if no transformation is specified, a column will reference the column specified in the Source column of the Mapping Grid.
More transformation examples can be found in Common Transformations.
Formatting Data Transformations
Depending on your data platform, you'll need to specify the format.
- Snowflake - Use single or double quotes. For example:
REPLACE({{SRC}}, 'Supplier#', '') - Databricks - Use backticks. For example:
ROUND(`forecast_hourly_metric`.`temperature`, 1)
Source Column Behavior
The source of a column is typically displayed in the Source column of the Mapping Grid. However, sources can also be defined within transformations.
-
Source added in the Transformation field:
-
The Source cell will be disabled.
-
On hover, more information about the source and an explanation for the cell's disabled state are shown.
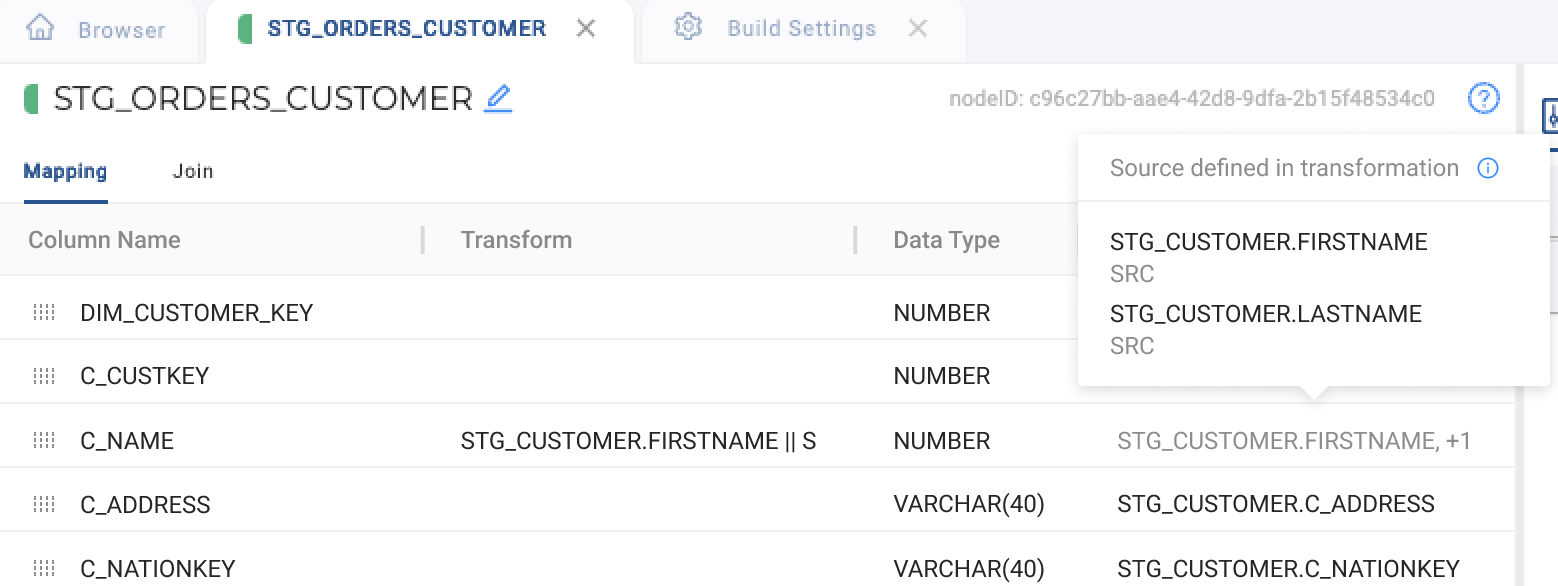
-
-
Source added in transformation using an alias:
-
The Source column will show the resolved source and the alias.
-
On hover, the alias will be displayed.
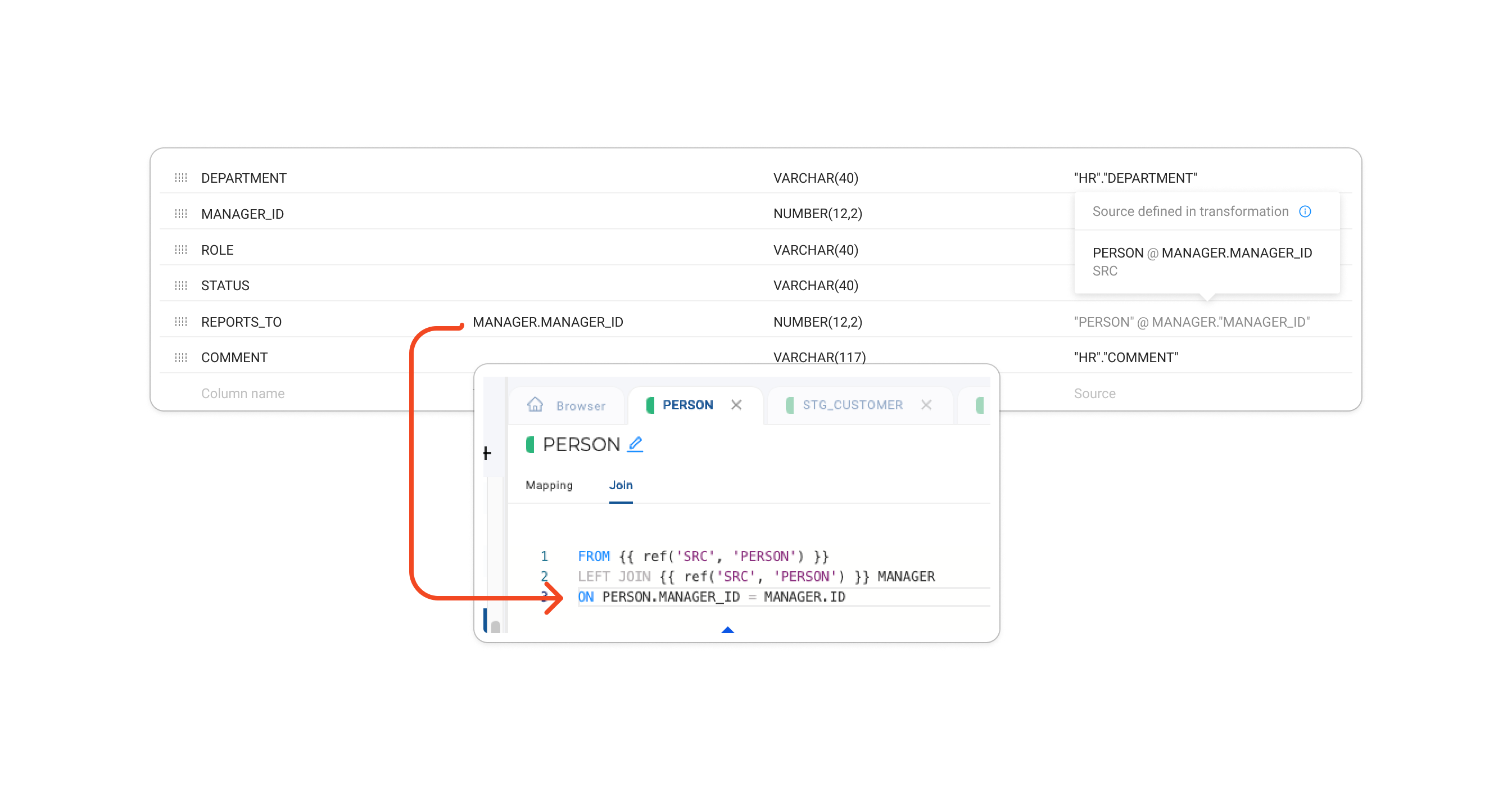
-
-
Source added in transformation and column referenced using alias and non-alias:
-
The same source will be shown twice, with one source indicated as aliased.
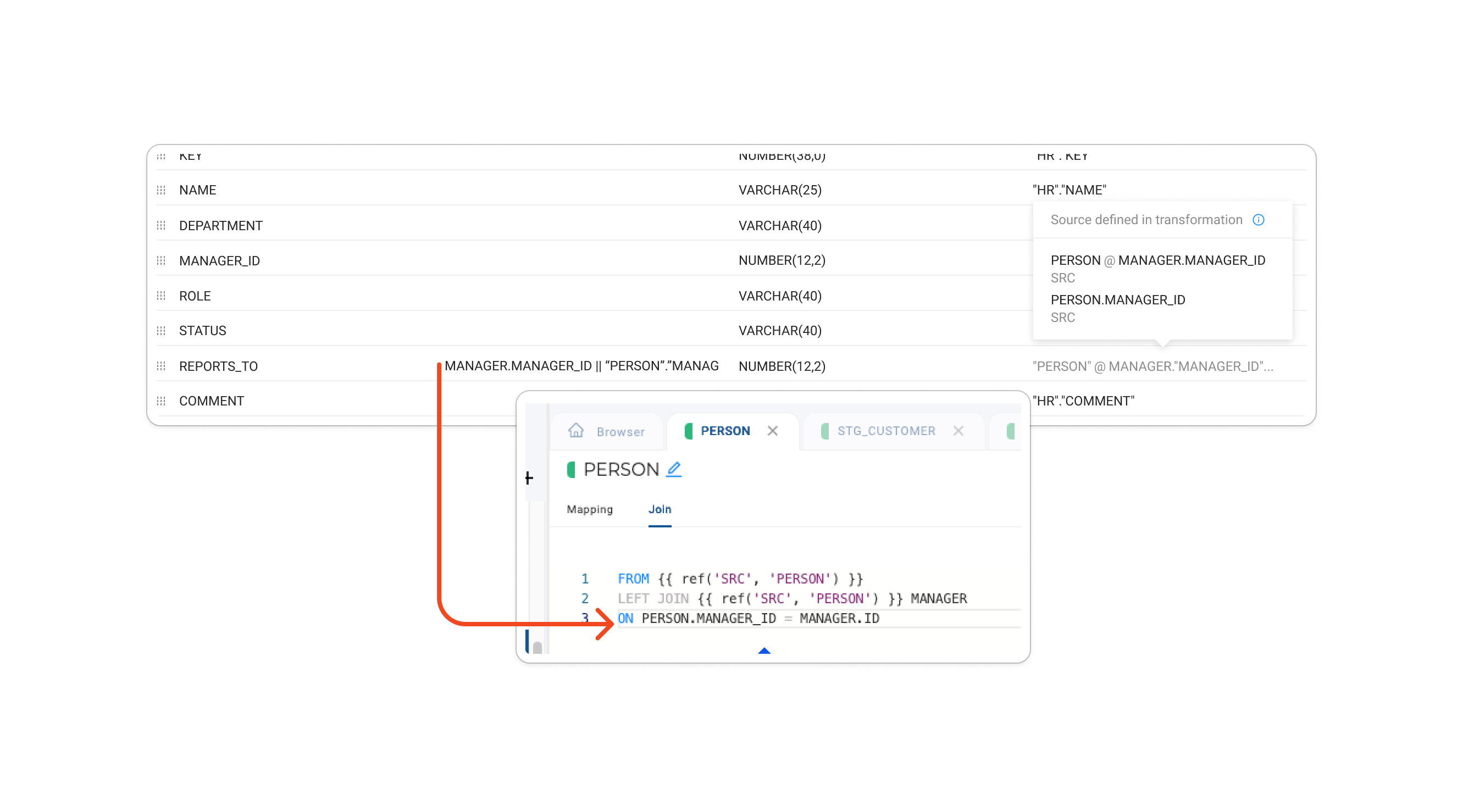
-
Best Practices
When working with column transformations, keep the following best practices in mind:
- Data Type Matching: Always set the data type of your column to match the expected output of your transformation.
- Use Macros for Repeated Logic: If you find yourself using the same transformation logic frequently, consider creating a Macro to encapsulate that logic and reduce code duplication.
- Be Aware of Source Definitions: Pay attention to where sources are defined (in the Source column or within transformations) to avoid conflicts and ensure your transformations behave as expected.
- Leverage Aliases: When working with complex transformations, using aliases can make your code more readable and maintainable.