Parsers
JSON Parsing
Open up any non-source node, right-click on the column, and select Derive JSON mappings.
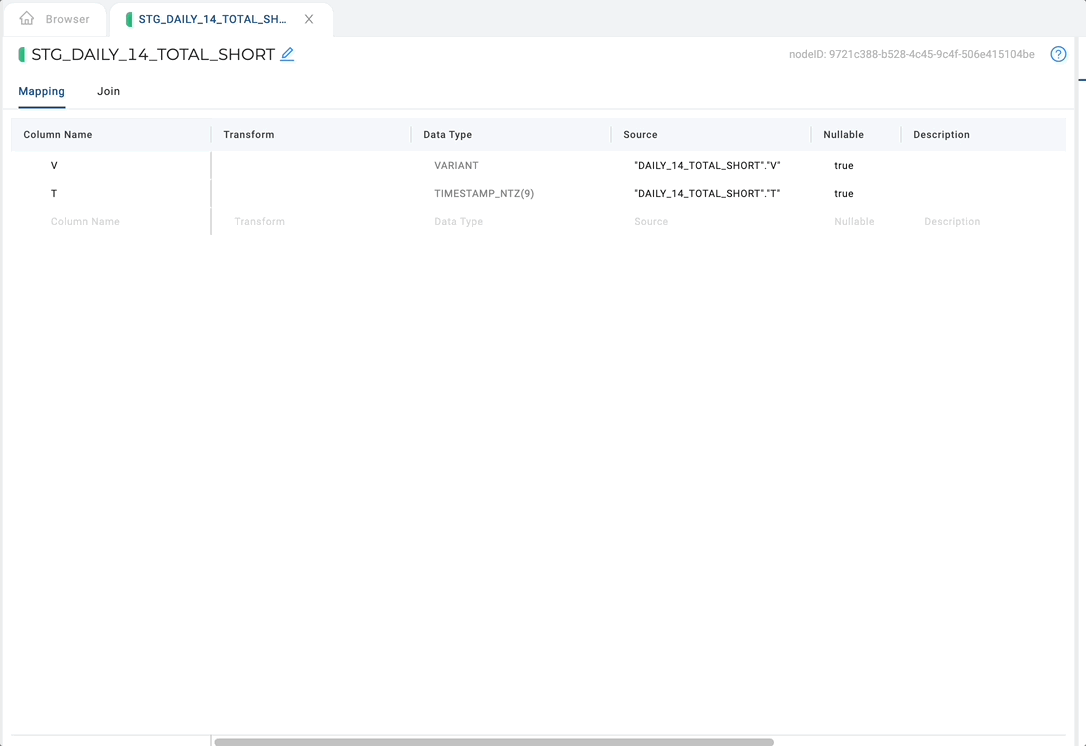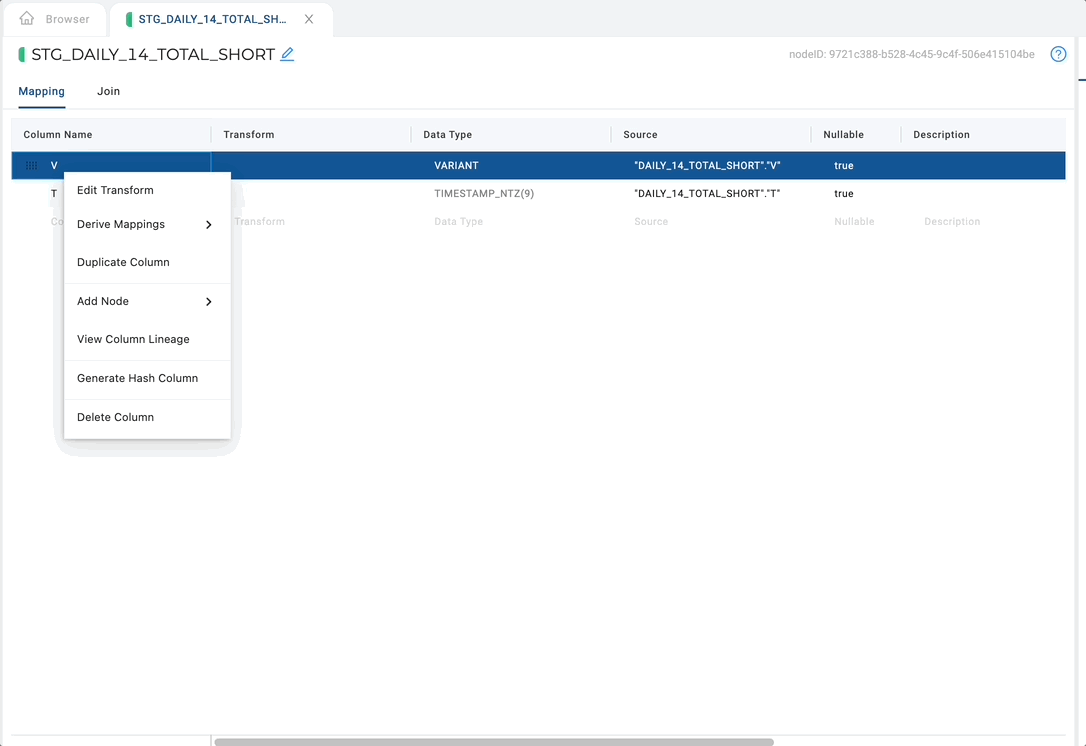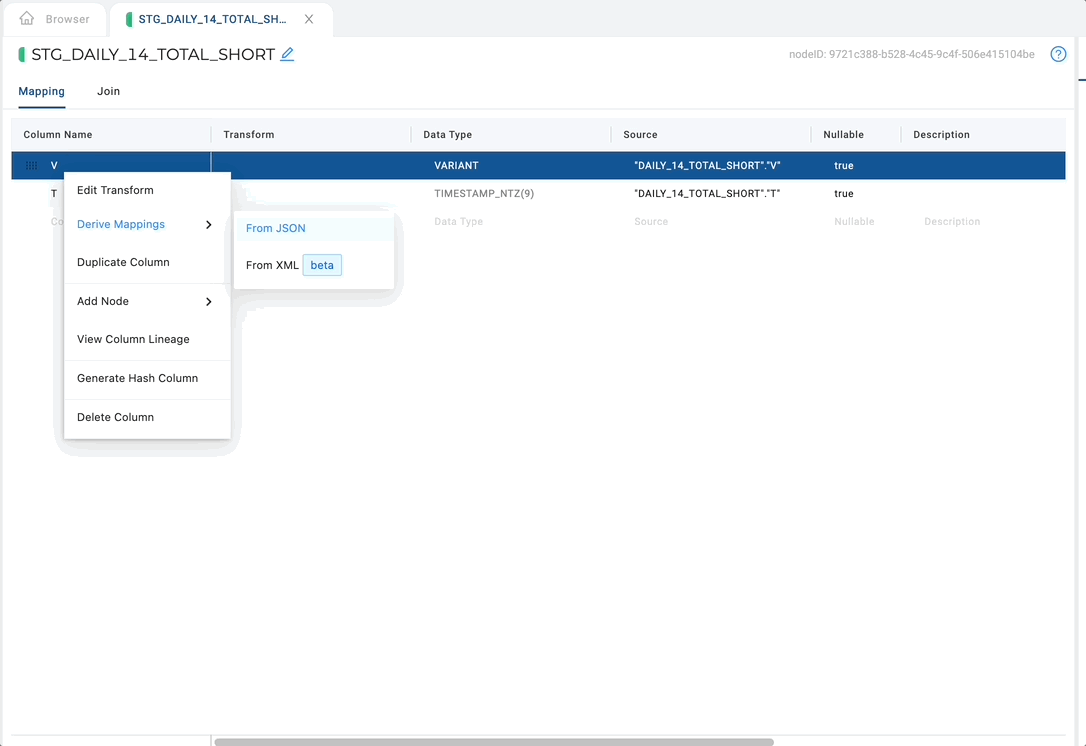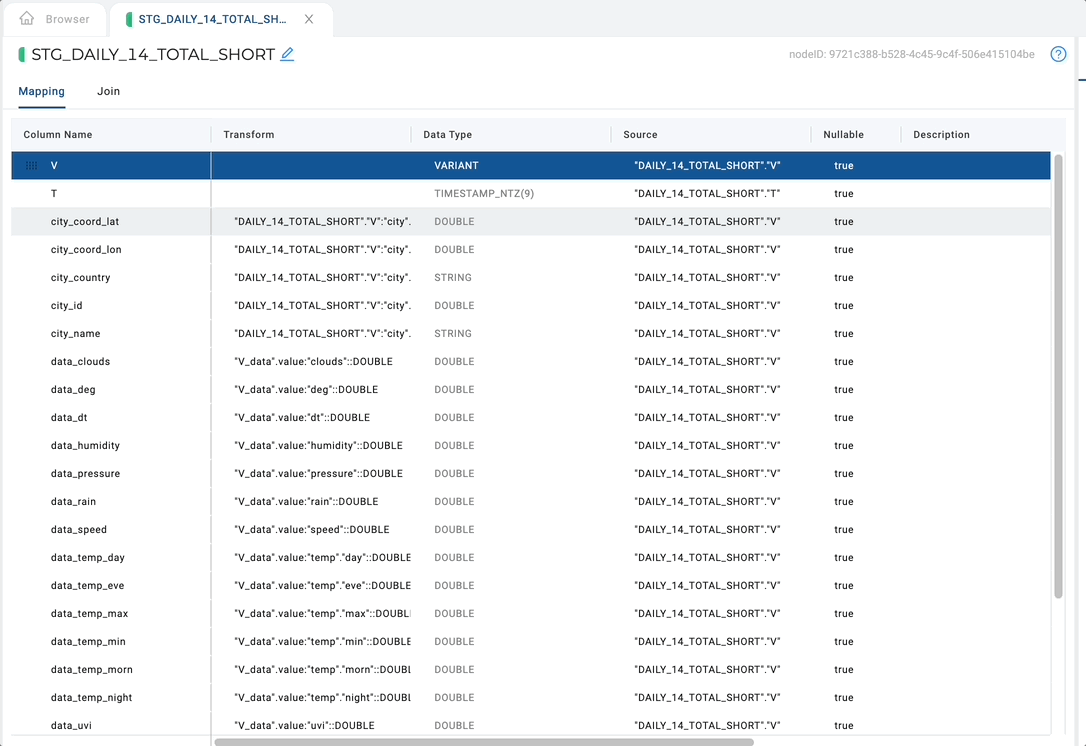
Derive JSON mappings will recursively:
- Create a column in the mapping grid for every primitive type (string, number, boolean, and null) within the object with the appropriate transform to parse that value.
- Flatten every JSON array using a table function in the Join Tab.
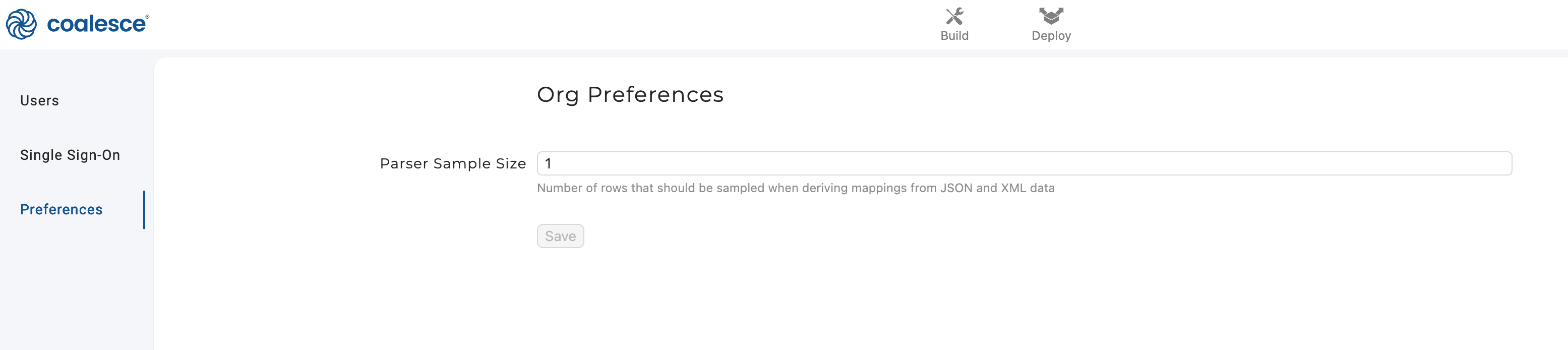
Setting JSON Sample Size
By default, the JSON parser captures only one record of the variant column. To scan for variation in the JSON shape across entries, the parser sample size (applies to both JSON and XML) can be increased via User Menu → Org Settings > Preferences. This preference is stored organization wide.
This number affects the number of rows we will attempt to scan for variances in JSON shape. Coalesce uses Snowflake's table sample to construct a sample of data. This is a sample of what is queried:
SELECT /* variant_column_name */ FROM /* fully qualified table */ SAMPLE ( /* sample size */ ROWS)
If a user enters a sample size larger than the number of rows in the data, all the rows in the data will be scanned for structure.
Data Type Mapping JSON
When the JSON parser scans for variances in JSON shape, a mapping occurs to convert JSON data types to the appropriate corresponding Snowflake data type.
| JSON Data Type | JSON Data Type Description | Snowflake Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| Number | Double-precision floating type | Double |
| String | Double-quoted Unicode with backslash escaping | String |
| Boolean | True or False | Boolean |
| Array | An ordered sequence of values | Flattens compound values into multiple rows |
| Object | An unordered collection of key:value pairs | Explodes compound values into multiple columns |
Prior to Coalesce version 5.4, JSON Numbers were mapped to Snowflake NUMBER(38,0), resulting in truncation of decimal places and converting them to integers.
XML Parsing (Beta Feature)
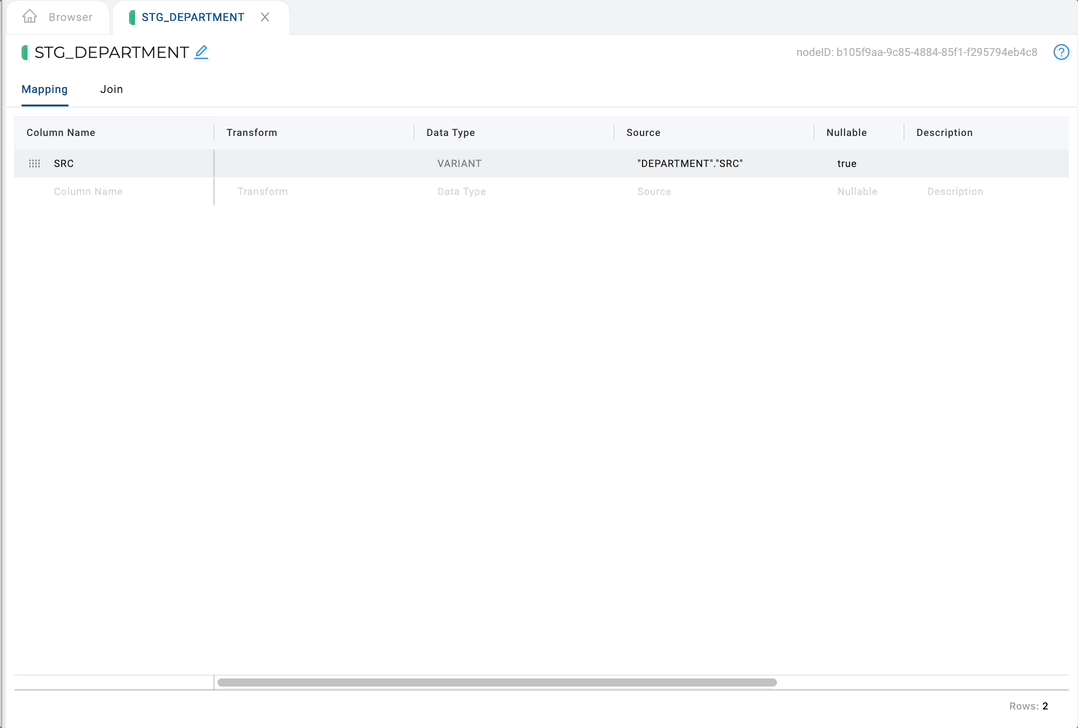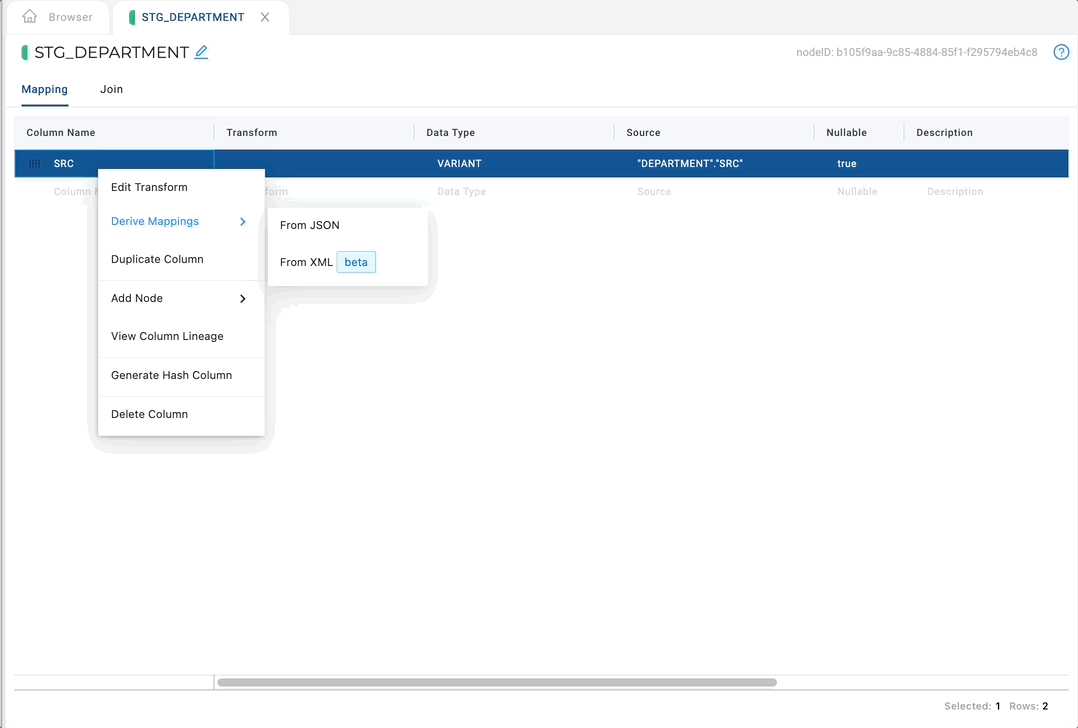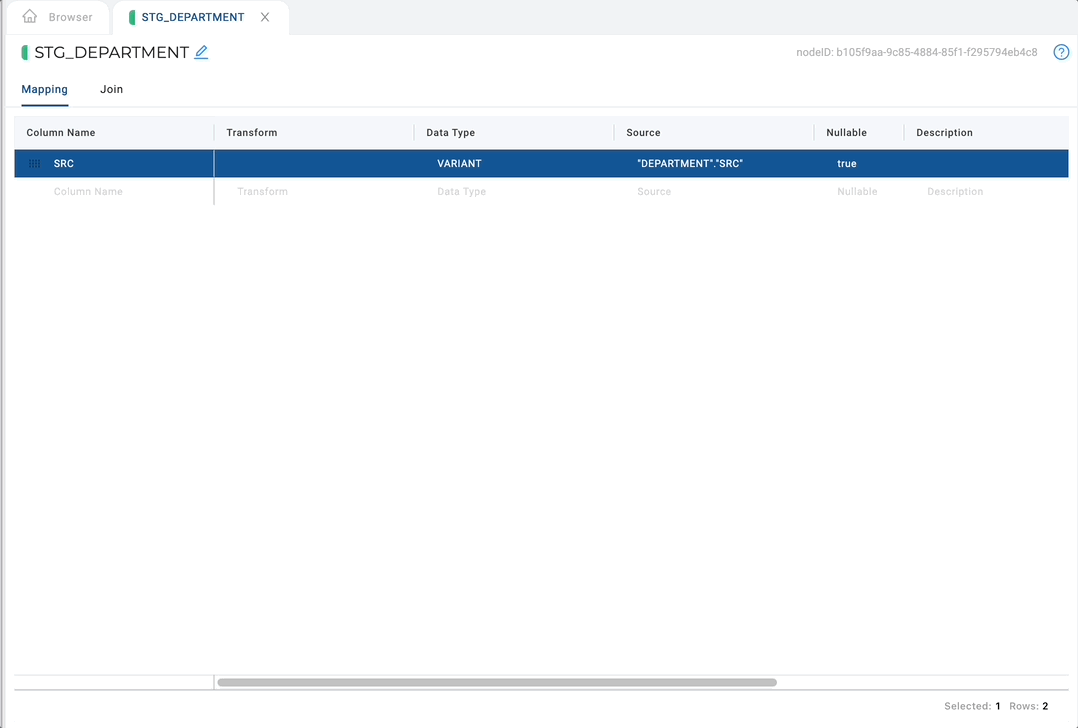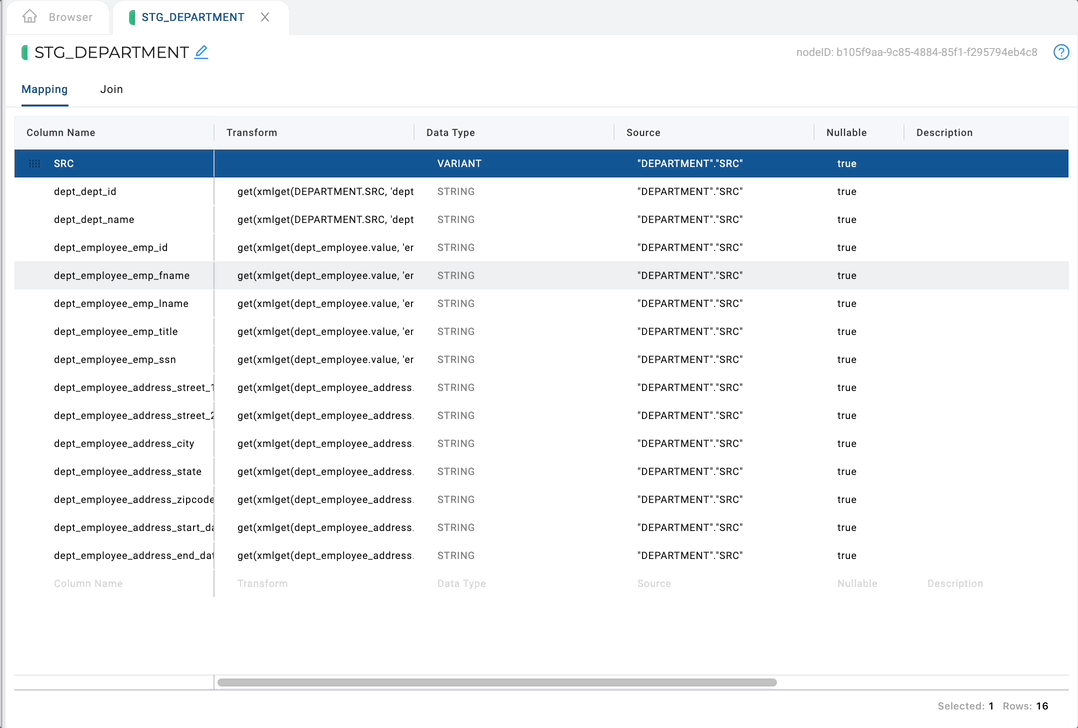
Open up any non-source node, right-click on the variant column, and select Derive Mappings > From XML.
SnowflakeOnly supported for Snowflake.
Derive XML mappings will recursively:
- Create a column in the mapping grid for every element and every attribute within the XML with the appropriate transform to parse that value.
- Flatten any XML sibling elements using a function in the Join Tab
Setting XML Sample Size
By default, the XML parser captures only one record of the variant column. To scan for variation in the XML shape across entries, the parser sample size can be increased via User Menu → Org Settings → Preferences. The parser sample size selected here applies to both JSON and XML and is used org-wide.
This number affects the number of rows we will attempt to scan for variances in XML shape. Coalesce uses Snowflake's table sample to construct a sample of data. This is a sample of what is queried:
SELECT /* variant_column_name */ FROM /* fully qualified table */ SAMPLE ( /* sample size */ ROWS)
If a user enters a sample size larger than the number of rows in the data, all the rows in the data will be scanned for structure.

When the XML parser scans for variances in XML shape, all values in the XML are converted to Snowflake strings.
Derive Mappings Bulk Operation
You can use bulk operations to derive mappings for multiple VARIANT columns simultaneously from the Column Grid View.
Requirements for Bulk Derive Mappings
All of the following conditions must be met to use the bulk derive mappings feature:
- All selected columns must have a
VARIANTdata type. - None of the selected columns can be from Source Nodes.
- The selected columns must be from different Nodes to prevent cartesian join conditions.
Using Bulk Derive Mappings
- Navigate to the Column Grid view.
- Select multiple columns that meet the requirements above using Command (Mac) or CTRL (Windows)
- Right click and select Derive Mappings, then choose either:
- From JSON
- From XML
Validation
The bulk derive mappings operation will validate your selection against the requirements before proceeding. If any of the conditions are not met (such as mixing VARIANT with other data types or selecting multiple columns from the same node), the operation will not be available.