Snowflake Key Pair Authentication
Coalesce supports Snowflake's key pair authentication for connecting Development Workspaces and Environments to Snowflake instances. Both encrypted and unencrypted private keys are supported. Encrypted keys have a corresponding passphrase that is required to use them, while unencrypted keys can be used directly. While keys are allowed to be encrypted with an empty passphrase by Snowflake, this is not supported in Coalesce and will result in an error.
We recommend using key pair authentication for automated actions.
Prerequisites
- Administrative access to your Snowflake account.
- Ability to create and manage Snowflake users.
- Access to Coalesce Build Settings for Environments or Workspaces.
- Understanding of your organization's security policies for key management.
Step 1: Get Your Snowflake Account Identifier
- Follow the instructions in Snowflake for Finding the organization and account name for an account.
- On the Account Details screen, copy the Account/Server URL. You'll need the first part. For example, if your URL is
ABC123-1234567.snowflakecomputing.com, you'll needABC123-1234567.
Step 2: Generate Key Pair in Snowflake
- Go through Snowflake’s key pair authentication steps to generate your keys.
- Make sure to generate a private key and save it for use in Coalesce.
- Generate your public key using the private key created for Coalesce.
- Assign the public key to your Snowflake user.
Step 3: Authenticate in Coalesce
- Navigate to Build Settings > Environments or Workspaces.
- Select Edit, , on the Environment or Workspace that you want to connect to Snowflake using key pair authentication.
- In Edit Environment or Workspace > User Credentials, select Authentication Type as Key Pair.
- Enter your Snowflake Username, Private Key, Private Key Passphrase (if applicable), Role and Warehouse into their respective fields and Save. Click Test Connection to ensure this works as expected.
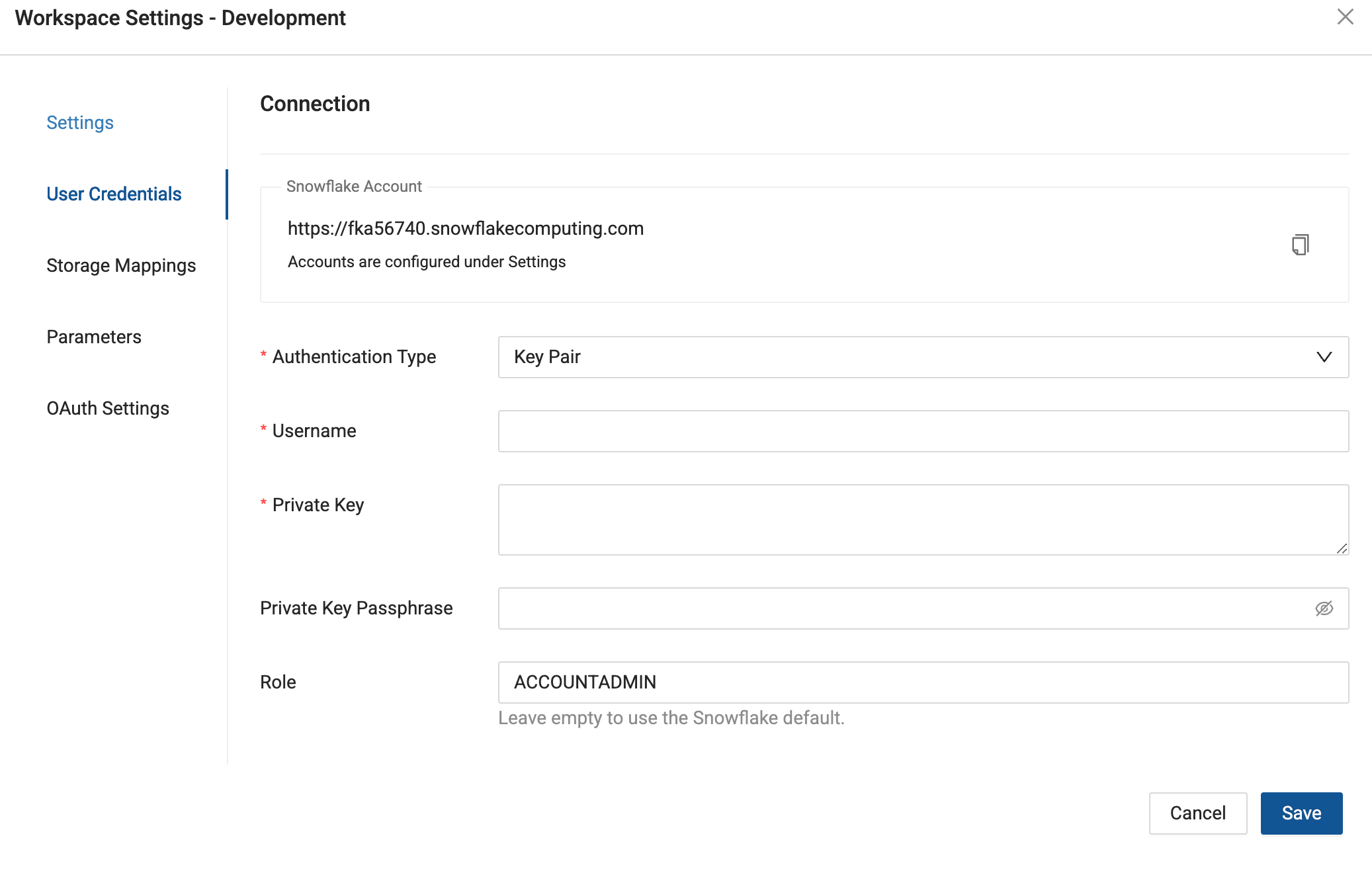
When entering your private key, make sure it's formatted properly. It must include the full private key including the lines BEGIN ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY and END ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY.
-----BEGIN ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----
Using Key Pair Authentication with Coalesce API
When using the Coalesce API to trigger Jobs programmatically, you can pass key pair credentials in your API requests.
API Request Structure
{
"runDetails": {
"jobID": "your-job-id",
"environmentID": "your-environment-id"
},
"userCredentials": {
"snowflakeAuthType": "KeyPair",
"snowflakeUsername": "YOUR_SERVICE_ACCOUNT",
"snowflakeKeyPairKey": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----",
"snowflakeKeyPairPass": "your-passphrase",
"snowflakeWarehouse": "YOUR_WAREHOUSE",
"snowflakeRole": "YOUR_ROLE"
}
}
Important API Considerations
-
Required fields:
- Always include
snowflakeUsernamewith KeyPair authentication. - Remove or omit
snowflakePasswordwhen using KeyPair. snowflakeAuthTypemust be exactly "KeyPair" (case-sensitive).snowflakeKeyPairPassis only required if the private key is encrypted.
- Always include
-
Key formatting for API:
- For JSON payloads, newlines within the key must be represented as
\n. - Preserve the full key structure including headers and footers.
- For JSON payloads, newlines within the key must be represented as
Integration Examples
PowerShell:
# Read and format private key
$privateKeyContent = (Get-Content "path/to/rsa_key.p8" -Raw).Replace("`r`n", "`n")
$body = @{
runDetails = @{
jobID = "your-job-id"
environmentID = "your-env-id"
}
userCredentials = @{
snowflakeAuthType = "KeyPair"
snowflakeUsername = "your_service_account"
snowflakeKeyPairKey = $privateKeyContent
snowflakeKeyPairPass = $keyPassphrase
snowflakeWarehouse = "your_warehouse"
snowflakeRole = "your_role"
}
} | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 3
$headers = @{
"Authorization" = "Bearer $coalesceBearerToken"
"Content-Type" = "application/json"
}
$response = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "https://your-instance.coalescesoftware.io/scheduler/startRun" -Method Post -Headers $headers -Body $body
Python (Apache Airflow):
import requests
from airflow.models import Variable
def trigger_coalesce_job():
# Get private key from Airflow Variable (stored securely)
private_key = Variable.get("SNOWFLAKE_PRIVATE_KEY")
payload = {
"runDetails": {
"jobID": Variable.get("COALESCE_JOB_ID"),
"environmentID": Variable.get("COALESCE_ENV_ID")
},
"userCredentials": {
"snowflakeAuthType": "KeyPair",
"snowflakeUsername": Variable.get("SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME"),
"snowflakeKeyPairKey": private_key,
"snowflakeWarehouse": Variable.get("SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE"),
"snowflakeRole": Variable.get("SNOWFLAKE_ROLE")
}
}
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {Variable.get('COALESCE_API_TOKEN')}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
response = requests.post(
"https://your-instance.coalescesoftware.io/scheduler/startRun",
json=payload,
headers=headers
)
return response.json()
Troubleshooting Common Issues
JWT Token Invalid Errors
Symptoms:
- "JWT token is invalid" error messages.
- Authentication failures despite correct credentials.
Solutions:
-
Verify key assignment in Snowflake:
DESC USER your_service_account;
-- Check that RSA_PUBLIC_KEY_FP is populated with a fingerprint value -
Validate account identifier: Ensure you're using the correct Snowflake account identifier format in your connection settings.
-
Check private key format:
- Ensure the private key includes proper header and footer lines.
- Verify there are no extra spaces, line breaks, or invalid characters.
- The key should be continuous text between the header and footer.
Private Key Parsing Failures
Symptoms:
- "Unable to parse private key" errors.
- Connection validation failures in Coalesce.
Solutions:
-
Test key validity:
# Verify your private key is valid
openssl rsa -in rsa_key.p8 -check -
Special character handling in passphrases: If your passphrase contains special characters such as
;or#, you may need to escape them:- Example:
hnw6a#nshould be entered ashnw6a\#n. - This is particularly important if you're storing the passphrase in configuration files.
- Example:
-
Format requirements:
- The private key must be in PEM format.
- Ensure no extra whitespace before or after the header and footer lines.
- Maintain original line breaks within the key content.
Environment-Specific Authentication Issues
Symptoms:
- Authentication works in development but fails in production.
- Cached credential issues after switching authentication methods.
Solutions:
-
Clear Environment cache: After changing authentication methods, redeploy your Environments. This ensures all cached credentials are refreshed.
-
Service account configuration:
- Use dedicated service accounts for automated processes
- Verify the service account has the necessary Snowflake roles assigned:
-- Check service account permissions
SHOW GRANTS TO USER your_service_account; -
Consistent authentication: Ensure all Environments use the same authentication method. Avoid mixing password and key pair authentication for the same user.
Connection Test Failures
Symptoms:
- Test Connection button fails in Coalesce UI.
- Error messages about invalid credentials or permissions.
Solutions:
-
Verify all required fields:
- Username must match the Snowflake user with the assigned public key
- Private key must be complete with headers and footers
- Passphrase must be provided if the key is encrypted
- Role must be a valid role assigned to the user
- Warehouse must exist and be accessible to the user
-
Check Snowflake user status:
-- Ensure user is not locked or disabled
SHOW USERS LIKE 'your_service_account'; -
Validate role and warehouse access:
-- Verify the user can access the specified warehouse
USE ROLE your_role;
USE WAREHOUSE your_warehouse;
Best Practices
Service Accounts
- Use dedicated Snowflake service accounts for automation.
- Apply the principle of least privilege when assigning Snowflake roles.
- Monitor service account usage and access patterns.
- Document which applications and processes use each service account.
Migration From Password Authentication
If you're migrating from password-based authentication to key pair authentication:
-
Preparation phase:
- Generate and test key pairs in Development Workspaces.
- Update any automation scripts or API integrations.
- Coordinate with your security team on key management procedures.
- Document the migration plan and rollback procedures.
-
Implementation phase:
- Deploy key pair authentication to Development Workspaces first.
- Test all Job executions and API integrations.
- Gradually migrate Production Environments.
- Maintain password authentication as a fallback during transition.
-
Validation phase:
- Monitor Job execution success rates.
- Verify all automated processes function correctly.
- Confirm all API integrations work as expected.
- Once stable, remove password-based authentication configurations.